microbiological testing

NISSUI
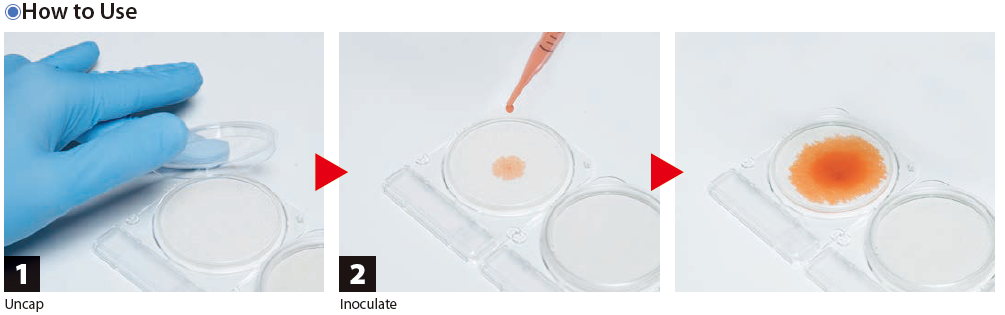

- Quick and easy to determine. Accurate counting.
- No need of complicated dilution and time-consuming steps.
- Small and delicate dry medium is convenient for storage and culturing.
- Small scale of sample can diffuse automatically.
- Compact dry can be kept in room temperature for one year.
- It is easy to pick colonies according to the color change of the medium.

Total Count
- Since tetrazolium salt is added in the medium, the colonies will be red and is easy to determine.
- Steps:
-
- 35 ± 2 ℃ incubation for 48 hr
- Count red colonies

EC ( E. coli, Coliform)
- E. coli and Coliform are presented in deferent colors according to the substrate of color presenting enzyme, Magenta-GAL and X-Gluc. It is easy to determine the colonies of E.coli or coliform by colors.
- Steps:
-
- 35 ± 2 ℃ incubation for 24 hr
- Count blue colonies as E. coli and total colonies as coliform.
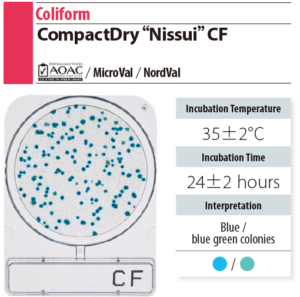
CF (Coliform)
- E. coli including E. coli O157 are presented in blue by adding X-GAL, which is the substrate of color presenting enzyme, into the medium.
- Gram negative bacteria other than E. coli are presented in white.
- Steps:
-
- 35 ± 2 ℃ incubation for 24 hr
- Count blue colonies as coliform.
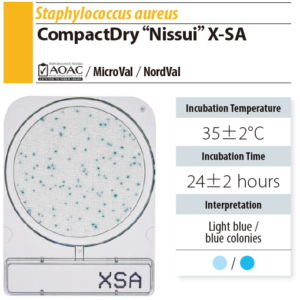
X-SA (Staphylococcus aureus)
- Staphylococcus aureus are presented in light blue or blue according to the substrate for color presenting enzyme.
- The bacteria other than Staphylococcus aureus are presented in white.
- Steps:
-
- 35 ± 2 ℃ incubation for 24 ± 2 hr
- Count light blue or blue colonies as SA.
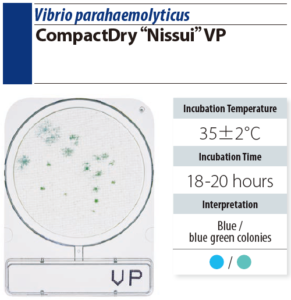
VP (Vibrio parahaemolyticus)
- Reformed according to TCBS agar. Inhibit the growth of bacteria other than Vibrio.
- V. parahaemolyticus are presented in blue according to the substrate of color presenting enzyme. Bacteria other than VP are presented in white.
- Steps:
-
- 35 ± 2 ℃ incubation for 18-20 hr
- Count blue colonies as V. parahaemolyticus
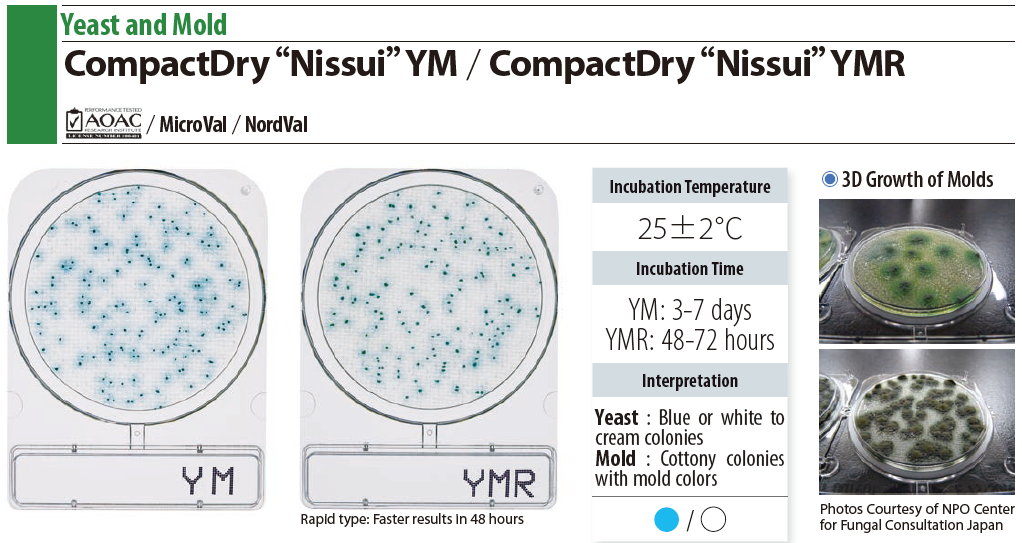
YM ( Yeast and Mold)
- The antibiotics in the medium inhibits the growth of bacteria.
- Most of the yeast presented in blue. Mold is black and cotton-like.
- Steps:
-
- 20 ~ 25 ℃ incubation for 3 ~ 7 days
- Count blue or white colonies as yeast and black cotton-like colonies as mold.
YMR ( Yeast and Mold rapid detection)
- The antibiotics in the medium inhibits the growth of bacteria.
- Most of the yeast presented in blue. Mold is black and cotton-like.
- Steps:
-
- 20 ~ 25 ℃ incubation for 2 ~ 3 days
- Count blue or white colonies as yeast and black cotton-like colonies as mold.

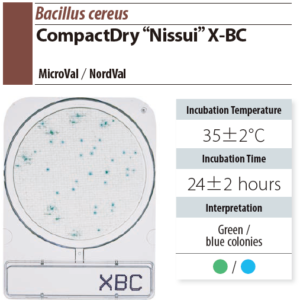
X-BC (Bacillus cereus)
- Other bacteria will not grow on the medium except Bacillus cereus.
- The colonies of Bacillus cereus will be green or blue.
- Steps:
-
- Incubate in 35 ± 2 ℃ for 24± 2 hr
- Count the green or blue colonies as Bacillus cereus.
SL (Salmonella)
- The lysine decarboxylase of Salmonella will increase the pH of the medium and change the color of the medium from purple to yellow.
- The colonies are presented in green by the substrate of the color presenting enzyme.
- Salmonella expresses H2S, which will change the color of colonies into black.
- Steps:
-
- Pre-incubation in 35 ~ 37℃ for 20 ~ 24 hr.
- Incubate on compact dry in 41 ~ 43℃ for 20 ~ 24 hr.
- Count the colonies of Salmonella according to the color of medium and colonies.

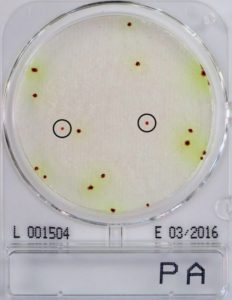
PA (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
- The antibiotics in the medium inhibits the growth of bacteria.
- Most of the yeast presented in blue. Mold is black and cotton-like.
- Steps:
-
- 34 ~ 36 ℃ incubation for 45 ~ 51 hours
- Count blue or white colonies as yeast and black cotton-like colonies as mold.
Microbes Detection Kit & Bacterialogical Testing Medium for Food and Environment
Microbes’ Incubation Medium and Reagents